Rwanda launches project to protect human health and the environment from the adverse effects of mercury pollution
The Rwanda Environment Management Authority (REMA), has launched the Minamata Initial Assessment (MIA) and National Action Plan (NAP) Projects.
Both projects were launched on June8, 2021 in line with the Minamata Convention on mercury, designed to protect human health and the environment from anthropogenic emissions and release of mercury and mercury compounds, that Rwanda acceded in June 2017.
Mercury is a naturally occurring element that is found in air, water and soil. Exposure to mercury – even small amounts – may cause serious health problems and is a threat to the development of the child before and after birth.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the inhaling mercury vapour can have harmful effects on the nervous, digestive and immune systems, lungs, kidneys and skin, and may be fatal. The inorganic salts of mercury are corrosive to the skin, eyes and gastrointestinal tract, and may induce kidney toxicity if ingested.
After becoming a part to Minamata Convention, Rwanda conducted a preliminary national survey to map out different institutions and priority areas suspected to have mercury, and mercury pollution, and these include Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM), health sector (thermometers, tensiometers, dental amalgams), industry sector (butchery, paints) among others.
“The MIA is one of the solutions that will help us to evaluate ourselves throughout national mercury inventory used in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold mining as well as in health sector. However, NAP will help us to have health status of the people working with these sectors and put in place the alternative technology aiming at phasing out the use of mercury” says Juliet Kabera, Director General, Rwanda Environment Management Authority (REMA).
The Minamata Initial Assessment project will raise awareness of health risks associated with mercury among the general public and government officials.
The artisanal and small-scale gold mining sector, along with health, ICT, Transport, water and informal sectors were identified as priority sectors related to the use of mercury.
The development of National Action Plans for artisanal and small-scale gold mining is a requirement under the Minamata Convention. Therefore, this project will support Rwanda to improve national capacity for managing mercury, and reduce the exposure of the people to mercury and the associated negative health consequences.
The two initiatives are being supported by the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR).
The Minamata Convention has a phased approach to reduce, and where possible, eliminate mercury use in key industrial sectors. It is also designed to systematically reduce emissions and releases to land and water and phase out the use of mercury where alternatives exist.
The Minamata Convention was adopted and opened for signature at the Conference of Plenipotentiaries held from 9 to 11 October 2013 in Minamata and Kumamoto, Japan and entered into force on 16 August 2017. Up to June 2018, 128 countries had signed the treaty and 94 had ratified it. As for now, 131 country have ratified the treaty and Rwanda became a Party on 29 June 2017.
To support the state parties to achieve the objective of the Convention, the Global Environment Facility (GEF) avails financial support to keep the momentum of making mercury history.
Topics
More posts
Rwanda hosts a two-day workshop for Negotiators of the High Ambition Coalition to End Plastic Pollution
Rwanda has from 14th to 16th February hosted a two-day workshop for negotiators of the High Ambition Coalition to End Plastic Pollution (HAC). The…
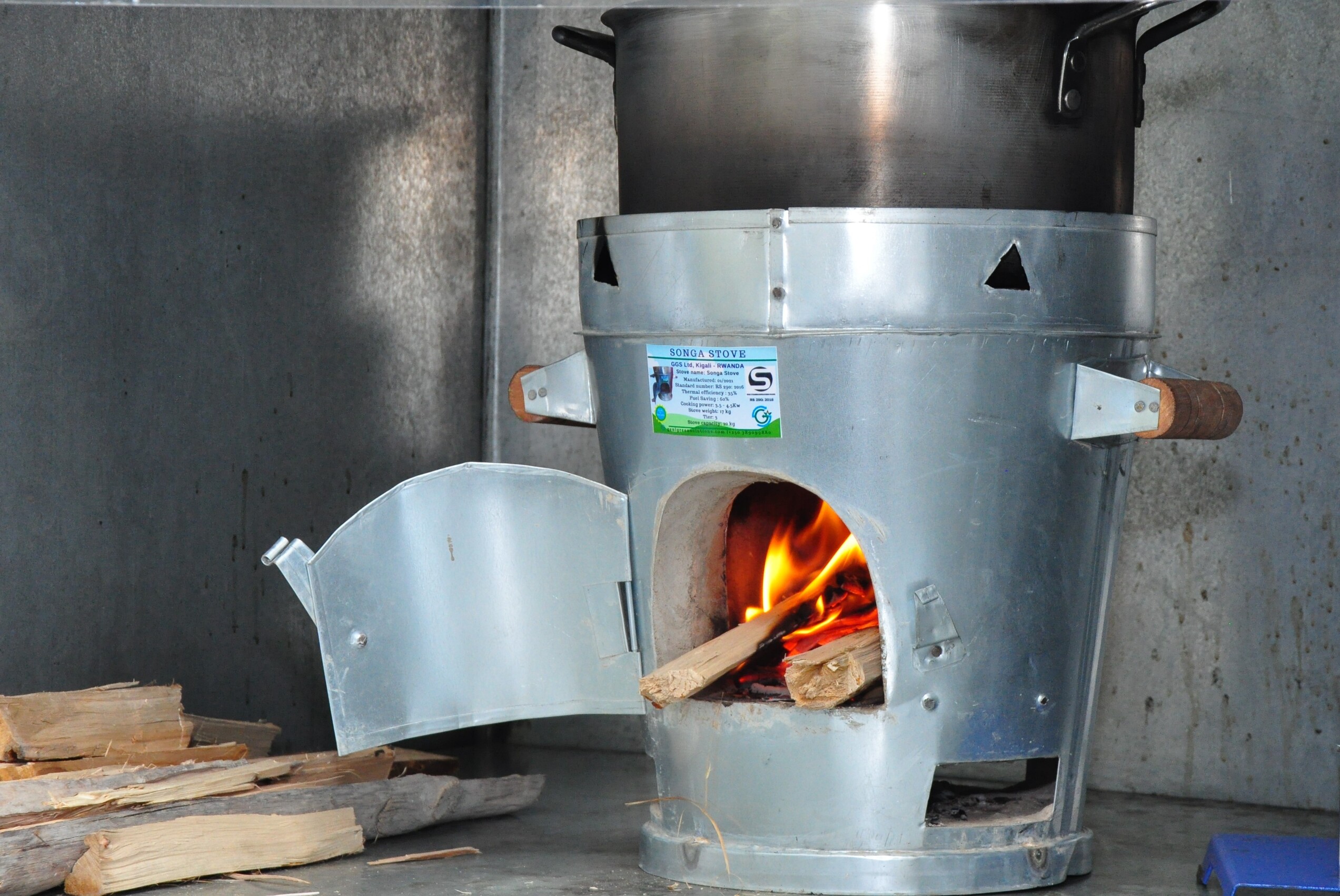
LDCF3 Project’s Improved Cookstoves: A Dual Solution for Climate Change and Human Health
In a ground-breaking move towards sustainable living, the Rwanda Environment Management Authority (REMA) is making significant strides in the fight…
From reluctance to acceptance: The LDCF3 Project beneficiaries embraces terraces for agricultural transformation
The beneficiaries of the Ecosystem/Landscape Approach to Climate Proof the Rural Settlement Programme of Rwanda, also known as LDCF3 Project, who…
Rwanda welcomes historic COP28 decision to transition away from fossil fuels
The Government of Rwanda has welcomed the ground-breaking decision made at the 28th Conference of the Parties (COP28) to the United Nations Framework…
Rwanda launches Carbon Market Framework to advance Climate Action for a Sustainable Future
Rwanda has today launched its National Carbon Market Framework in a significant stride towards a greener and more sustainable future. The framework…
Over 45 professionals complete a capacity-building program in climate change analysis and reporting
Kigali, 17 November, 2023- Kigali, REMA, in collaboration with the African Institute for Mathematical Sciences in Rwanda(AIMS_Rwanda), celebrated the…
REMA’s LDCF3 Project distributes 5,000 improved cookstoves to beneficiaries to tackle climate change
The Rwanda Environment Management Authority distributes 5,000 improved cookstoves to beneficiaries of the Landscape Restoration Approach to Climate…
BIOFIN’s Technical Advisor on Environmental Finance visits Rwanda to foster stakeholder engagement
The Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN)’s Technical Advisor on Environmental Finance for Africa, Mr. Bruno Mweemba recently visited Rwanda from…
World Ozone Day: REMA recognizes students and lecturers with technologies and eco-friendly cooling solutions
Rwanda in September 2023 joined the rest of the world to mark the World Ozone Day with the theme “Montreal Protocol: Fixing the Ozone layer and…