How Rwanda is Using Climate Change Data and Projections to Plan for the Future
Kigali, 29 October, 2021- In 2011, Rwanda adopted a Green Growth and Climate Resilience Strategy to become a developed, climate-resilient and low-carbon economy by 2050. To achieve this goal, the government and its stakeholders are working to reduce emissions and foster climate resilience.
One of the strategy’s programmes of action is ‘Climate Data and Projections’, which was designed to maintain climate change records and provide data to help the country prepare for a warmer world through new technologies and capacity building.
Having access to climate data and projections is essential for Rwanda to respond to climate change using evidence-based policy making. Therefore, a number of institutions came together to track and manage climate related data, including Meteo Rwanda, the Ministry of Education, the Rwanda Environment Management Authority, the Rwanda Green Fund and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). This effort includes regular measurements, weather forecast, data management, information sharing and climate knowledge and education.
Work is underway to build Rwanda’s capacity to advance the national adaptation planning process and is being implemented by Meteo Rwanda and the Rwanda Environment Management Authority. One of activities is climate change projections for Rwanda on different timescale such as 2030, 2040, 2050 and 2080. Those projections will be used to develop climate risk assessments and to inform policy-makers and planners about climate risks.
In addition to this ground-breaking project, here are three other initiatives that are enabling Rwanda to better understand its climate today and more accurately predict how it will change into the future.
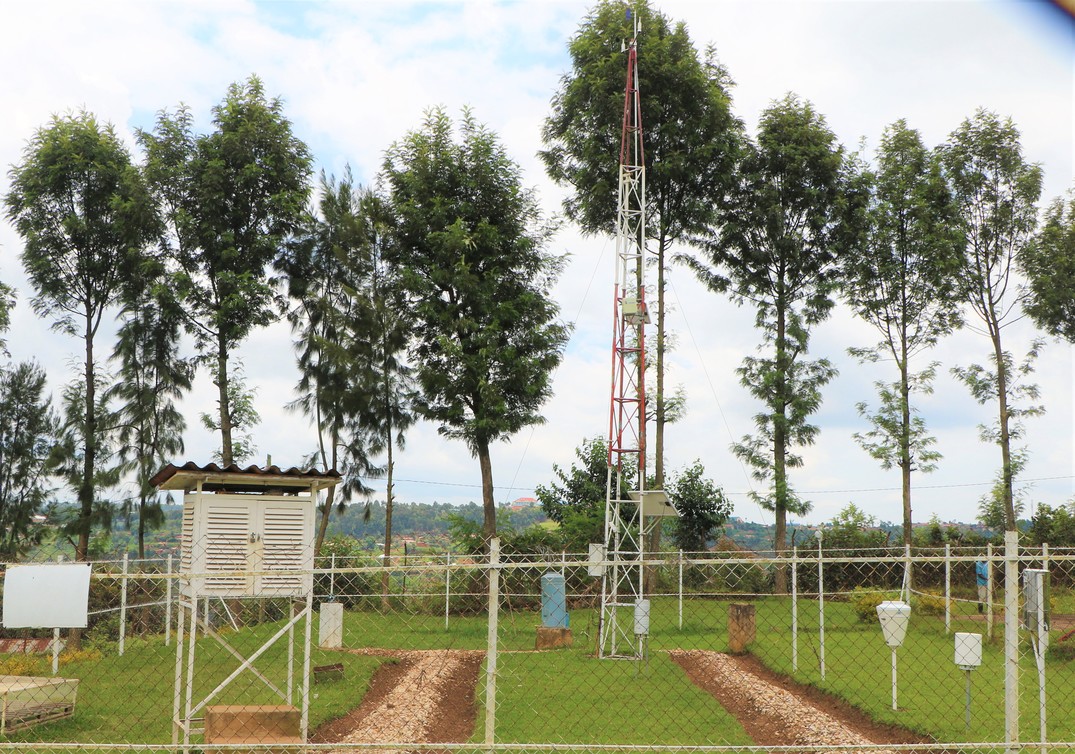
1. Rwanda Climate Change Observatory
The Rwanda Climate Change Observatory is a world-class project initiated in 2011 by the Ministry of Education in collaboration with the MIT to measure climate change on Mount Mugogo in terms of greenhouse gases (GHG), meteorological parameters, other climate change factors as well as building skills in storing, processing and archiving GHG data from different sectors.
The Climate Change Observatory is part of WMO's Global Atmosphere Watch network measuring greenhouse gases and air quality. As a World Meteorological Organisation Global Atmosphere Watch station, it contributes to an international network of observation systems supporting the global response to climate change.
This initiative has strengthened research on climate change and atmospheric sciences, presented education opportunities for Rwandans and trained them on effective climate data maintenance and analysis.
2. Investing in Meteo Rwanda forecasting and climate modeling
The Rwanda Meteorology Agency (Meteo Rwanda) provides accurate, timely weather and climate information services for safety of life, property and for socio-economic development of the country. The agency collects, gathers and accesses meteorological data from weather stations around the country. The data are analysed in parallel with data from other sources to generate the weather forecast of different ranges of time (nowcast, short, medium and long ranges forecast), with the aim of supporting socio-economic development.
Given the importance of weather and climate data for responding to climate change, significant investments have been made to boost the capacity of Meteo Rwanda. This has been done through an investment from the Rwanda Green Fund called ‘Strengthening Rwanda's Weather and Climate Services to Support Development’. This initiative provided new monitoring equipment and increased the technical skills that lead to improvement of the range of weather and climate information available to inform decision making at all levels in Rwanda,
This project installed climate change and air quality monitoring infrastructure and provided training to inform decision-making and enforcement activities. The infrastructure provides data for regulators and is being used as a research tool in higher learning institutions. Data is now being provided to climate modellers to increase climate change consequence modelling in Rwanda and across the region.
3. Building a nationwide Air Quality Index
Rwandans can now access real-time air quality information thanks to a new website and mobile application launched by the Ministry of Environment, Rwanda Environment Management Authority and Rwanda Meteorology Agency.
The countrywide air quality monitoring system provides data on the quality of the air in twenty-three sites across the country. The Air Quality Monitoring System was developed through the Air Quality and Climate Change Monitoring Project, which has been funded by the Rwanda Green Fund (FONERWA). It was designed in collaboration with Massachusetts Institute of Technology and implemented by Rwanda Environment Management Authority and the Ministry of Education.
The system provides real-time Air Quality Index (AQI) for each station in both numerical and color code format. The system highlights the dominant air pollutant which is responsible for air quality degradation during the reported period for each station. It will help Rwanda to compare ground observations data with satellite data through remote sensing technology to verify their accuracy.
The system strengthens Rwanda’s existing field installed air quality monitoring network by providing online access to pollution readings from each station as well as data management including data sharing mechanisms.
Visit the Air Quality Monitoring System here:
● Website: www.aq.rema.gov.rw
● Mobile App (Android): play.google.com/store/apps/details;
Learn more about Rwanda’s efforts to use data to prepare for the future at www.meteorwanda.gov.rw.
Topics
More posts
Rwanda hosts a two-day workshop for Negotiators of the High Ambition Coalition to End Plastic Pollution
Rwanda has from 14th to 16th February hosted a two-day workshop for negotiators of the High Ambition Coalition to End Plastic Pollution (HAC). The…
LDCF3 Project’s Improved Cookstoves: A Dual Solution for Climate Change and Human Health
In a ground-breaking move towards sustainable living, the Rwanda Environment Management Authority (REMA) is making significant strides in the fight…
From reluctance to acceptance: The LDCF3 Project beneficiaries embraces terraces for agricultural transformation
The beneficiaries of the Ecosystem/Landscape Approach to Climate Proof the Rural Settlement Programme of Rwanda, also known as LDCF3 Project, who…
Rwanda welcomes historic COP28 decision to transition away from fossil fuels
The Government of Rwanda has welcomed the ground-breaking decision made at the 28th Conference of the Parties (COP28) to the United Nations Framework…
Rwanda launches Carbon Market Framework to advance Climate Action for a Sustainable Future
Rwanda has today launched its National Carbon Market Framework in a significant stride towards a greener and more sustainable future. The framework…
Over 45 professionals complete a capacity-building program in climate change analysis and reporting
Kigali, 17 November, 2023- Kigali, REMA, in collaboration with the African Institute for Mathematical Sciences in Rwanda(AIMS_Rwanda), celebrated the…
REMA’s LDCF3 Project distributes 5,000 improved cookstoves to beneficiaries to tackle climate change
The Rwanda Environment Management Authority distributes 5,000 improved cookstoves to beneficiaries of the Landscape Restoration Approach to Climate…
BIOFIN’s Technical Advisor on Environmental Finance visits Rwanda to foster stakeholder engagement
The Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN)’s Technical Advisor on Environmental Finance for Africa, Mr. Bruno Mweemba recently visited Rwanda from…
World Ozone Day: REMA recognizes students and lecturers with technologies and eco-friendly cooling solutions
Rwanda in September 2023 joined the rest of the world to mark the World Ozone Day with the theme “Montreal Protocol: Fixing the Ozone layer and…